While striving to up your health regimen, knowing the standard tests and others that could be necessary to improve your endeavors is advisable. Your doctor can recommend a test, and by its sound, cause panic as you fear that there’s something that’s considerably wrong with your health. For example, carotid ultrasound sounds scary, but there could be nothing to be concerned about, rather than a precaution test. If you’ve pursued a carotid ultrasound course, you understand the importance of the tests, when needed the most, and how it improves your health measures. Here is a quick dive into what carotid ultrasound entails.
What is carotid ultrasound?
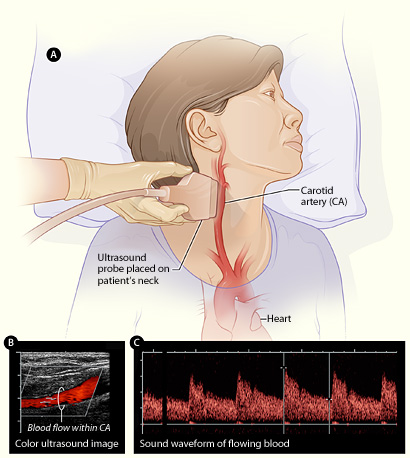
The test is a painless, safe, and non-invasive test that utilizes sound waves to examine your carotid arteries’ blood flow. Carotid arteries are found at each side of your neck. The two arteries deliver blood from the heart to the brain. Should there be concerns, such as narrowing or blockage, the test shows it, advising your doctor on measures to rectify the issue. If left unattended, the affected blood flow puts you at risk of a stroke. Among the top reasons your doctor can recommend a carotid ultrasound is if you experience a transient ischemic attack or stroke. It is also a commonly recommended test if you have existing medical concerns that increase the risk of suffering a stroke, such as diabetes, coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and a family history of heart conditions or strokes, to mention a few. Other situations that may necessitate carotid ultrasound include;
- Determining the effectiveness of a stent, a mesh tube that’s placed aimed at improving blood flow through the arteries
- After surgery, to monitor and establish if there’s good blood flow or concerns such as plaques are present
- Detect any carotid artery abnormality disruption effective blood flow
- Check and if any, locate clotted blood (hematoma) affecting the blood flow through the arteries
What can you expect from the procedure?
A sonographer carries out the test. After pursuing the carotid ultrasound course, you’ll be a qualified technician referred to as a sonographer. The sonographer utilizes a transducer, a hand-held device that emits sound waves, recording the echo as the waves bounce off your tissues, blood cells, and organs. The sonographer will ask you to lie on your back, and they may position your head to facilitate smooth access to the side of the neck. They’ll then apply a warm gel to the skin above the carotid artery’s position. The gel is intended to facilitate better ultrasound wave transmission back and forth. After the gel application, the technician will gently press the transducer against the side of the neck. Shouldn’t experience any discomforts during the process, and if any, tell the technician immediately.
A computer translates the echoed sound waves into a live-action image on the monitor. An expert, such as a radiologist, uses Doppler ultrasound, showing blood flowing through your arteries, and in this case, the flow is translated into a graph. The test takes a brief moment, typically 30 minutes.
After the radiologist (an imaging tests expert) translates the results, they could discuss the findings with you directly or communicate with the doctor who ordered the test. The test could reveal that there is no need for concern or that you are at risk of a stroke. If it is established that you are at risk, your doctor can recommend a range of therapies following your situation and the severity of the carotid artery’s blood flow blockage. Some of the common therapies include;
- Regular physical exercise and maintaining a healthy weight range
- Dietary measures such as recommending more fruits and veggies, cereals, and whole-grain bread, and limiting saturated fat
- Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
If the situation is more demanding, the doctor could recommend medication and procedures including;
- Medication to control blood pressure and lower blood cholesterol
- Treatment to prevent blood clots
- Surgical operations to remove carotid artery plaques, also known as carotid endarterectomy or open up and support the carotid arteries, also known as angioplasty stenting
In a situation where the carotid ultrasound was a follow-up of surgery, your doctor will inform you if the procedure worked. While carotid ultrasound is effective, you might need more tests for clearer results. Other tests that may be required after the carotid ultrasound includes MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) and CTA scan (Computerized tomography angiogram scan).
Caring for your overall well-being includes dealing with tests, some invasive and others like a carotid ultrasound that painless and non-invasive. With information on such tests at your fingertips, you can comfortably navigate the medical arena and supercharge your health regimen.
Featured Image Source: Wikimedia Commons