In an agrarian society like India, it is interesting to note that, though almost everybody including the Government of India talks about technology, infrastructure, modernization of agriculture sector, and something as significant as Fasal Bima yojana, nobody is willing to educate a Kissan (farmer) about three basic things that is ruining his life forever – How to buy seeds for commercial farming? Where to buy high yielding seed varieties? And when to cultivate these high yielding variety seeds to get the maximum profits in their area?
Remarkably, if a farmer is trained in the above three aspects, none of the farmers would want to quit farming, forget committing suicides. In fact, none of the farmers would then will have to send their children to the cities to make money for earning a livelihood. In a series of articles on commercial farming, we would focus on the first aspect i.
e. How to buy seeds for commercial farming:
The Key Factors Essential for Buying Seeds:
How to Buy Seeds? Know your Location
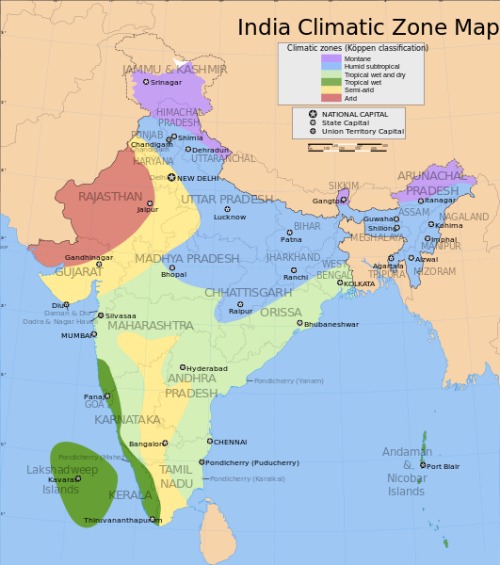
First thing first! Before you start, you need to know your area well, both topographically as well as geographically. According to the Koppen climate classification system, India is divided into 6 areas (refer Map) :
Image Courtesy: via Wikimedia Commons
- Tropical Wet (Humid)
Western and Southern Parts of Maharashtra, Western parts of Karnataka, Kerala and Goa (entire)
- Tropical Wet and Dry
Maharashtra (except southern and western area), South-western Parts of Madhya Pradesh, Central region of Karnataka, Northern and Eastern Parts of Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Parts of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana (except west and south region), Parts of Chhattisgarh (except north region), Odisha, low lying areas of West Bengal.
- Tropical Semi-Arid Steppe
Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Parts of Western Uttar Pradesh, Eastern region of Rajasthan, Parts of Gujarat, Parts of Madhya Pradesh, Parts of Tamil Nadu, Parts of Andhra Pradesh, Parts of Telangana, a very small area in Maharashtra, Parts of Karnataka.
- Sub-Tropical Humid
Entire Uttar Pradesh except some parts in western UP, Parts of Uttarakhand (From Centre towards south), Parts of Madhya Pradesh (Central and Eastern), Bihar, Parts of Jharkhand, Parts of Chhattisgarh, Parts of West Bengal, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura, Nagaland, Assam, Manipur, Parts of Arunachal Pradesh, Southern Parts of Sikkim
- Mountainous
Upper Parts of Sikkim, Parts of Arunachal Pradesh, Parts of Uttarakhand, Parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir
- Arid or Desert
Parts of Rajasthan and Parts of Gujarat
Next, you’ll have to shortlist only those seeds that are suitable for your region. In case, the farmer uses a seed of humid sub-tropical in semi-arid, it will affect the yield and productivity of the crop drastically. The reason being, the seeds are manufactured based on the temperature and the climatic condition of different regions. So, a farmer has to inquire about the seed before plantation.
Buy Seeds for Commercial Farming According to the Season of Sowing
In India, there are three cropping seasons – Kharif (time of sowing – May end to July), Rabi (time of sowing – October to November) and Zaid also known as Summer(time of sowing February to March). The seed manufacturing organizations and companies breed seeds based on these seasons. So, if a farmer has to grow tomatoes in Kharif season, he has to ensure that the tomato seed he is buying is of Kharif season and not of Rabi or Zaid.
Most of the farmers in India grow plants from any seed that is available in the seed store. Next, they complain about poor productivity.
It is, therefore, the duty of the Central as well as State Government to educate the farmers on this aspect rather than spending crores of money on advertising on things that are totally irrelevant to farmers and farming in general.
Buy Seeds According to Your State’s Geographical Zone
It is important to ensure that you buy seeds that are suitable to the sowing season of your region/area. Seeds of Kharif season of Maharashtra may not be suitable to Uttar Pradesh in Kharif season and vice versa.
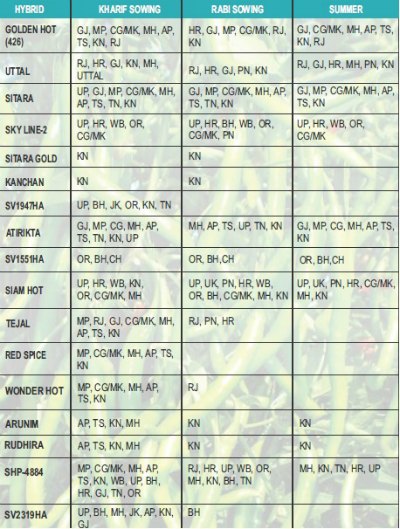
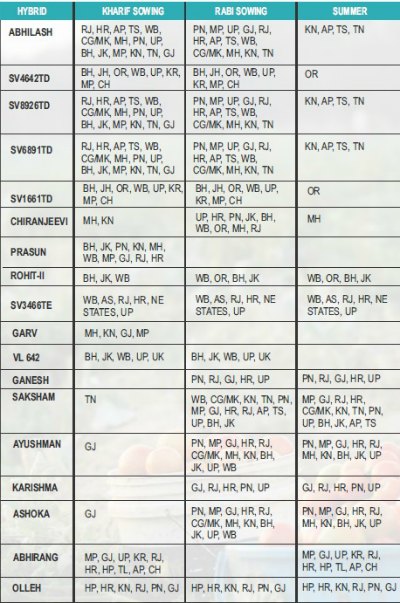
Let me give you an example, you are a farmer of Uttar Pradesh and you wish to grow Chilli. Next, you search for Chilli seeds that can be grown in Uttar Pradesh. You’ll be surprised to see that the high yielding variety you want to sow might not be suitable for the season you want to sow. For instance, the Chilli seed variety ‘Sitara’of Monsanto India (brand Seminis) cannot be sown in Rabi in Uttar Pradesh, it can be sown only in Kharif season. However, ‘Sitara’ can be grown in all the season in Maharashtra and Gujarat. On the contrary, Skyline-2 can be grown in all the three seasons in the state of Uttar Pradesh whereas seed Atirikta can only be sown in Rabi and Kharif in Uttar Pradesh. (Check out the chart below of Seminis Chilli Cultivar)
(Check out the chart below of Seminis Tomato Cultivar)
Image Source: Bighaat.com
Just imagine the productivity and result if you as a farmer due to lack of knowledge buy seeds of Atirikta and sow the same during the Summer season (Zaid). This has been a plight of a majority of the farmers in India.
Know How to Buy Seeds According to the Rainfed Areas
India is broadly classified into two areas – Irrigated Area and Rain-Dependent area. The irrigated areas have the facilities to feed the crop with water from various sources. However, the rain-dependent areas are those areas which are totally dependent on rains. These rain-dependent areas are called as rainfed areas.
There was a time when rainfed region had very limited options for farming. However, today, many of the organizations and companies in India are manufacturing seeds that are primarily meant for rainfed regions. So, while buying, a farmer of the rain-fed area should buy seeds meant for the area only then can he expect plantation. On the contrary, a farmer living in the area with good irrigation facility should avoid buying rainfed seeds as it can affect the yield of the crop significantly.
In our next article, we shall focus on our next topic – “Where to buy high yielding seed varieties (cultivar)”?
Do Not Miss Reading:
Plant Nutrients Vs Pesticides: Know How Mineral Nutrients Prevent Plant Disease!